What is EPAT Shockwave Therapy
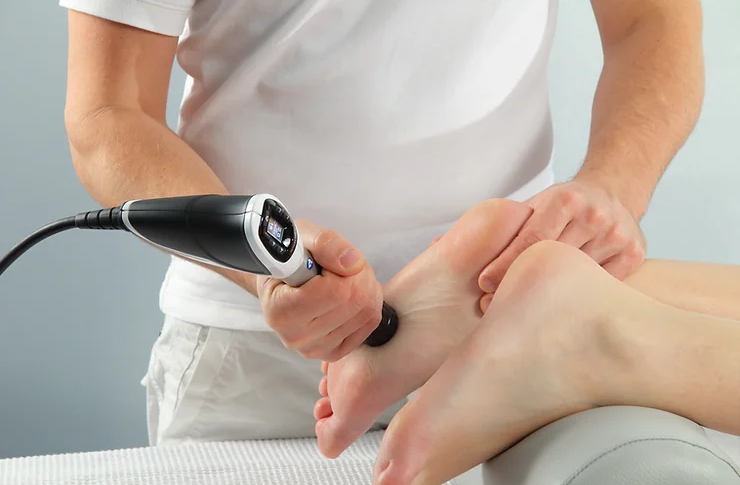
Do you have persistent pain? Are you seeking an alternative to surgery? If so, EPAT Shockwave Therapy could be the solution for you!
EPAT shock wave therapy, also known as extracorporeal shock wave therapy, is becoming increasingly popular in the realm of physiotherapy. EPAT therapy is a non-invasive pain relief treatment that employs shockwaves. It is an FDA-approved treatment that has been demonstrated to be useful in the treatment of a range of ailments such as plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendonitis, tennis elbow, and others.
This article will explain what EPAT Shockwave Therapy is and how it can help you get rid of chronic pain!
What is EPAT Shockwave Therapy – A brief
Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology, or EPAT, is a non-invasive, FDA-approved treatment for a variety of musculoskeletal problems.
Historically, shockwave therapy was used to break down kidney stones, allowing patients to avoid painful surgical procedures. Now, physiotherapists, osteopaths, podiatrists, and other medical practitioners utilize it to treat a variety of disorders involving tendons, muscles, and even bones.
By increasing blood flow and breaking down scar tissue, EPAT stimulates the body’s natural healing mechanism. Plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendinitis, tennis elbow, and other conditions can be treated using EPAT. EPAT has been established in studies to be an effective treatment with a high success rate.
In one study, 91% of EPAT patients reported significant improvements in their symptoms. For people seeking an alternative to surgery or other intrusive therapies, EPAT is a safe and effective therapy choice.
Types of Shockwave therapy?
Shock wave therapy is classified into two types.
#1 Radial Shockwave Therapy
Radial is used to treat superficial skin problems near the skin’s surface.
#2 Focused Shockwave Therapy
A focused shockwave can treat a broader spectrum of illnesses by treating deeper regions of concern.
How does it work?
Shockwaves are used in EPAT therapy to stimulate the body’s natural healing mechanism. The shockwaves boost blood flow and tear down scar tissue, which can aid with pain relief and movement.
The mechanism of action of EPAT is mostly understood but not completely. In the process sound waves are considered to cause the release of Endorphins, which are natural pain relievers produced by the body.
Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that shockwave plays a vital role in collagen production and proliferation, which is critical in tissue repair, particularly in muscles and tendons; indeed, musculotendinous tissue appears to be the primary focus for shockwave therapy.
Finally, EPAT is a non-invasive, drug-free treatment that does not require anesthesia or surgery. It is usually administered in three doses, each lasting about fifteen minutes.
What to Expect?
Shockwave therapy is without a doubt one of the most successful and well-established clinical treatments for the treatment of chronic soft tissue injuries.
The positive benefits of EPAT are frequently felt after only three treatments. Although some patients experience instant pain relief following therapy, it can take up to four weeks for pain relief to begin.
It is critical to understand that EPAT is not a “cure” for your illness, but rather a means to provide pain relief and improve function. The operation can relieve pain and restore complete mobility, enhancing your quality of life.
More than 80% of individuals treated report being pain-free or experiencing significant pain relief. EPAT is a therapeutic option that is both safe and effective, with a high success rate. This FDA-approved technology was created in Europe and is now utilized all over the world.
Each EPAT device is designed with a wealth of medical experience, cutting-edge engineering, and superior quality, and comprehensive clinical investigations and tests have proved its safety and efficacy.
Who is a Good Candidate for EPAT Shockwave Therapy
Your podiatrist will determine whether Shockwave treatment is appropriate for you, but candidates typically include people who have had chronic pain for several months and have not received relief from standard treatments.
Shockwave therapy may potentially improve established treatment procedures by shortening recovery durations. Other prospects include people who need to return to work or physical activities immediately.
Shockwave therapy is usually seen to be safe and non-invasive, however, it may not be appropriate for pregnant women, children, or those with blood-clotting issues.
Otherwise, anyone suffering from Achilles tendinitis, heel spur syndrome, or plantar fasciitis is a candidate for EPAT.
Is there any Pain or Discomfort Associated with the Treatment
EPAT is a non-surgical treatment with few risks and negative effects. In certain situations, individuals may have minor discomfort for a few days following treatment, and/or their skin may become bruised or red.
Shockwave is not as frightening as it sounds. In certain circumstances, you may experience pain at first, but the therapy is provided with a low level of energy initially, which increases as your body adjusts, so there’s nothing to worry about.
How long will the results last
According to the research and experience with shockwave therapy, most patients will see a significant clinical benefit in their pain 6 to 8 weeks after treatment. According to studies, this pain relief might last for months or even years following your final shockwave session.
Conclusion
If you are suffering from chronic issues such as soft tissue injuries or tendinitis and have exhausted all other treatment choices, shockwave therapy may be an option for you. Shock wave therapy is an excellent alternative to surgery or when other common therapies, such as pain medication and steroid injections, are no longer effective and have unwanted side effects and hazards. Speak with your doctor right away to discover if this therapy can help you get relief.
Continue reading some articles here on how to manage different soft tissue injuries.

